CHM 301 Organic Chemistry 11: Acid Chloride
CHM 301 Organic Chemistry 11: Acid Chloride
Uploaded by
WAN NUR AISYAH WAN AZIZANCopyright:
Available Formats
CHM 301 Organic Chemistry 11: Acid Chloride
CHM 301 Organic Chemistry 11: Acid Chloride
Uploaded by
WAN NUR AISYAH WAN AZIZANOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Copyright:
Available Formats
CHM 301 Organic Chemistry 11: Acid Chloride
CHM 301 Organic Chemistry 11: Acid Chloride
Uploaded by
WAN NUR AISYAH WAN AZIZANCopyright:
Available Formats
CHM 301
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 11
ACID CHLORIDE
SUBTOPICS
1.0 General formula
2.0 Nomenclature: IUPAC and
common name
3.0 Preparation
4.0 Reactions
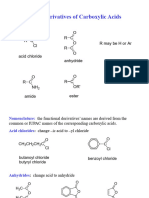
1.0 GENERAL FORMULA
2.0 NOMENCLATURE
General formula O
R C Cl
Nomenclature
i) IUPAC name
- acid or acyl chlorides are named by replacing the
suffix “-ic acid” with “-yl chloride”.
O O
H3C C OH H3C C Cl
ethanoic acid ethanoyl chloride
- carbonyl carbon atom is designated as C1.
O O
6 5 4 3 2
CH3CH2CHCH2CCl CH3CH=CCH2CH2CCl
5 4 3 2 1 1
CH3 CH3
3-methylpentanoyl chloride 4-methyl-4-hexenoyl chloride
O O 2N O
C Cl C Cl
benzoyl chloride 3-nitrobenzoyl chloride
- for acids that are named as alkanecarboxylic
acids, the acid chlorides are named by using the
suffix –carbonyl chloride.
O
C Cl
cyclopentanecarbonyl chloride
ii) Common name:
O Br O
CH3CH2CCl CH3CHCH2CCl
IUPAC : propanoyl chloride IUPAC : 3-bromobutanoyl chloride
Common: propionyl chloride Common: ß-bromobutyryl chloride
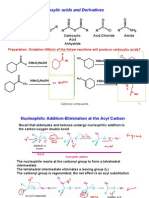
3.0 PREPARATION OF
ACID CHLORIDES
PREPARATION OF ACYL CHLORIDES / ACID
CHLORIDES
Carboxylic acids reacts with phosphorus (v) chloride (PCl5) or
sulphur dichloride oxide (thionyl chloride) or phosphorus
trichloride (PCl3) at room temperature to form acyl chloride.
In the case of benzoic acid, the reaction mixture is heated.
O O
R C OH PCl5 R C Cl POCl3 HCl
carboxylic acids acid chlorides
O O
R C OH SOCl2 R C Cl SO2 HCl
carboxylic acids acid chlorides
O O
3 R C OH PCl3 3 R C Cl H3PO3
carboxylic acids acid chlorides
Examples:
O O
CH3 C OH SOCl2 CH3 C Cl SO2 HCl
ethanoic acid ethanoyl chloride
O O
C OH SOCl2 C Cl SO2 HCl
benzoic acid benzoyl chloride
4.0 REACTIONS OF ACYL CHLORIDES
1. Hydrolysis
2. Ammonolysis
3. Alcoholysis
4. Friedel-Craft acylation
4.1 HYDROLYSIS
Acyl chlorides react readily with water to form carboxylic acids.
Occurs in aqueous base and at room temperature.
When an acyl chloride is added with water, carboxylic acid and
steamy acidic fumes of HCl are formed.
O O
R C Cl H-OH R C OH HCl
O
O H+ HCl
R C OH
R C Cl H-OH
OH- O
R C O Cl-
MECHANISM FOR HYDROLYSIS OF ACYL
EXAMPLE:
CHLORIDES
O H O
H3C C Cl CH3 C OH HCl
O H
Step 1: Water attacks the carbonyl carbon causing the
C=O to cleave.
O H O
CH3 C Cl CH3 C Cl
O H
O H
Step 2: The elimination step occursHwhen π-bond forms
between C and O and the chloride ion is removed.
O
O H
CH3 C Cl
CH3 C O H Cl
O H
H
Step 3: H+ ion is removed by chloride ion to
yield HCl.
O H O
CH3 C O H Cl CH3 C O H HCl
4.2 AMMONOLYSIS
Acyl chlorides react with ammonia, primary and secondary
amines to form amides.
The reaction is rapid and produce excellent yield.
O O
+ -
R C Cl 2NH3 R C NH2 NH4 Cl
O O
R C Cl 2RNH2 R C NHR RNH3+Cl-
O O
R C Cl 2R2NH R C NR2 R2NH2+Cl-
MECHANISM FOR AMMONOLYSIS OF ACYL
EXAMPLE:
CHLORIDES
O O
H3C C Cl 2NH3 CH3 C NH2 NH +Cl-
4
Step 1: NH3 attacks the carbonyl carbon causing the C=O to
cleave. O O
CH3 C Cl NH3 CH3 C Cl
NH3
Step 2: The elimination step occurs when π-bond forms
between C and O and the chloride ion is removed.
O O
CH3 C Cl CH3 C NH3 Cl
NH3
Step 3: H+ ion is removed by chloride ion to yield
amide and HCl.
O H O H
CH3 C N H Cl CH3 C N H HCl
H
HCl NH3 NH4+Cl-
The removal of H+ ion may also be done by the
NH3 molecule.
O H O H
CH3 C N H NH3 CH3 C N H NH4+
H
+
NH4 + Cl- NH4+Cl-
4.3 ALCOHOLYSIS
Acyl chloride react with an alcohol to produce an ester.
Does not require catalyst even through alcohol is a weak
nucleophile because acyl chloride is highly reactive.
The reaction is irreversible unlike the reaction of carboxylic
acid with alcohol.
Pyridine is added to prevent side reaction between HCl and
ROH.
O O
pyridine
R C Cl R'-OH R C OR' HCl
When pyridine is present, it removes HCl by reacting with it to
yield pyridinium chloride salt.
N HCl NHCl
Acyl chloride also reacts with phenol to
produce ester.
The reaction is not as vigorous as the
reaction of acyl chloride with alcohol.
O OH O
pyridine
H 3C C Cl OCCH3 HCl
MECHANISM FOR ALCOHOLYSIS OF ACYL
EXAMPLE:
CHLORIDES
O O
pyridine
H3C C Cl CH3CH2 O H CH3 C OCH2CH3 HCl
Step 1: Ethanol attacks the carbonyl carbon causing the
C=O to cleave
O O
H3C C Cl CH3CH2 O H CH3 C Cl
H O CH2CH3
Step 2: The double bond of carbonyl carbon
regenerates and pushes chloride ion out of the
molecule.
O O
CH3 C Cl CH3 C OCH2CH3 Cl
H O CH2CH3 H
Step 3: H+ ion is removed by chloride ion to
yield HCl.
O O
CH3 C OCH2CH3 Cl CH3 C OCH2CH3 HCl
H
4.4 FRIEDEL-CRAFTS ACYLATION
An effective method of adding acyl group on the
aromatic ring.
Treating aromatic compound with an acyl chloride
in the presence of a catalyst, AlCl3 to produce
ketone.
O
H C R
O
AlCl3
R C Cl HCl
benzene ketone
EXAMPLES:
O
C CH3
O AlCl3
HCl
CH3CCl
H3 C O
AlCl 3 O H3 C
Cl H3 C
-CH3: ortho and para director O
NO2 O
NO2
AlCl3
Cl
-NO2: meta director
O
The End….TQ
Love Organic Chemistry …in shaa Allah
You might also like
- Good Loo GuideDocument54 pagesGood Loo Guidealex_allen_3No ratings yet
- 6 8 Acyl Chlorides and Acid AnhydridesDocument5 pages6 8 Acyl Chlorides and Acid AnhydridesPedro Moreno de SouzaNo ratings yet
- Preparation of Aldehydes and Ketones: Video 1Document15 pagesPreparation of Aldehydes and Ketones: Video 1Ain Atikah ZulkepliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16Document87 pagesChapter 16Hafizszul FeyzulNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acid DerivativesDocument38 pagesCarboxylic Acid DerivativesshaikmguNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acids and Its Derivatives PDFDocument58 pagesCarboxylic Acids and Its Derivatives PDFAniruddha Kawade100% (2)
- Nomenclature Esters: AlkylDocument35 pagesNomenclature Esters: AlkylAstri MaulidaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Aldehydes KetonesDocument51 pagesChapter 1 - Aldehydes KetonesSarathy Hari KumarNo ratings yet
- UNG - Carbox 3Document35 pagesUNG - Carbox 3ShofiakhoerunnisaNo ratings yet
- DerivativesDocument58 pagesDerivativesravi_balaskarNo ratings yet
- Reactions of Carbonyl CompoundsDocument75 pagesReactions of Carbonyl Compoundszekarias wondafrashNo ratings yet
- Hydroxyl at I OnDocument60 pagesHydroxyl at I OngbgbkrishnaNo ratings yet
- OxidationDocument38 pagesOxidationSayed Newaj ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Carbonyl Alpha-Substitution Reactions %D9%85%D9%87%D9%85Document79 pagesCarbonyl Alpha-Substitution Reactions %D9%85%D9%87%D9%85Hamdy SolimanNo ratings yet
- Che 176 Carboxylic Acids-2Document67 pagesChe 176 Carboxylic Acids-2BalogunNo ratings yet
- Addition of HBR To Alkenes inDocument33 pagesAddition of HBR To Alkenes inolkokoooNo ratings yet
- Carbonyl Compounds 1Document23 pagesCarbonyl Compounds 1Gowri ShankarNo ratings yet
- Carbonyl PostDocument66 pagesCarbonyl Postapi-3767370100% (2)
- Aromatic ReactionsDocument70 pagesAromatic ReactionsGabriel BandaNo ratings yet
- Alcohols and EthersDocument51 pagesAlcohols and EthersnanaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Ketones and Aldehydes: Organic Chemistry Anmol UpadhyayDocument82 pagesUnit 2 Ketones and Aldehydes: Organic Chemistry Anmol UpadhyayanmolNo ratings yet
- Module 16-Haloform Reactions For Methyl KetonesDocument7 pagesModule 16-Haloform Reactions For Methyl Ketoneszedbored0No ratings yet
- Part 2-Chapter 3Document52 pagesPart 2-Chapter 3Nguyen NhatNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Carboxylic Acids Chm301Document32 pagesChapter 3 Carboxylic Acids Chm301Arricson HunterNo ratings yet
- 6carboxylic Acids PDFDocument29 pages6carboxylic Acids PDFsharmimiameerasanadyNo ratings yet
- 11 Chemistry Notes Ch13 HydrocarbonsDocument23 pages11 Chemistry Notes Ch13 HydrocarbonsSahil ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Ethers: C H CH CH OC H 2-Ethoxy PropaneDocument12 pagesEthers: C H CH CH OC H 2-Ethoxy Propanekumar swamyNo ratings yet
- Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers Chapter7-8Document43 pagesAlcohols, Phenols and Ethers Chapter7-8Shourav SarkarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 ALCOHOLDocument65 pagesChapter 1 ALCOHOLNURUL AINUN MUHAMMAD NOR100% (1)
- Aromatic Hydrocarbons Complete LectureDocument29 pagesAromatic Hydrocarbons Complete LectureHamza RiazNo ratings yet
- 1e Aldehyde & KetoneDocument48 pages1e Aldehyde & KetoneJonathan Wyatt100% (1)
- 10 Haloalkanes and Haloarenes 1 MK QuestionsDocument42 pages10 Haloalkanes and Haloarenes 1 MK QuestionsPriyanks RoutNo ratings yet
- Aldehyde and KetonesDocument41 pagesAldehyde and KetonesJerome DimaanoNo ratings yet
- 5 Aldehydes and Ketones-Structure and PreparationDocument41 pages5 Aldehydes and Ketones-Structure and PreparationKeshav JoshiNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes and KetonesDocument41 pagesAldehydes and KetonesJerome DimaanoNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic AcidsDocument26 pagesCarboxylic Acidsapi-3734333100% (1)
- Ald&Ketone IDocument41 pagesAld&Ketone IHarsha Y MNo ratings yet
- Carbonyl Compounds Aldehydes and Ketones2Document6 pagesCarbonyl Compounds Aldehydes and Ketones2Sachitra WijethungaNo ratings yet
- +2 NEET IntelliQuest PCB-3 (28.01.2021) AnsKey - 10645292Document3 pages+2 NEET IntelliQuest PCB-3 (28.01.2021) AnsKey - 10645292swap2005sharmaNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acid Derivatives: Nucleophilic Acyl SubstitutionDocument30 pagesCarboxylic Acid Derivatives: Nucleophilic Acyl SubstitutionSudrajatNo ratings yet
- Chemistry XII CHP 7Document6 pagesChemistry XII CHP 7amanrajbhar7068No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Alcohols 2024Document65 pagesChapter 1 - Alcohols 2024isfaNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acid Jeemain - GuruDocument26 pagesCarboxylic Acid Jeemain - GuruKumar KumarNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acid Derivatives: Reactivity Considerations: O C O Y R Z C O + YDocument11 pagesCarboxylic Acid Derivatives: Reactivity Considerations: O C O Y R Z C O + YShreeyesh BiswalNo ratings yet
- Reactions of Alcohol: Oxidation ReductionDocument18 pagesReactions of Alcohol: Oxidation ReductioncikguhafidzuddinNo ratings yet
- Aldehids and KetonesDocument47 pagesAldehids and Ketonesistri kyungsoNo ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry Keypoints Revision Questions Chapter 12Document20 pages12 Chemistry Keypoints Revision Questions Chapter 12sangam patraNo ratings yet
- Carbonyl CompoundsDocument50 pagesCarbonyl CompoundsFariz SharudinNo ratings yet
- Alkyl HalidesDocument26 pagesAlkyl Halidesharerambaghel906No ratings yet
- Alkyne-Anna IN CLASS 1Document26 pagesAlkyne-Anna IN CLASS 1Siti Farhanah Mohd NasirNo ratings yet
- OrganicCompoundsContainingHalogensDPPII-2024SolutionsCopyDocument9 pagesOrganicCompoundsContainingHalogensDPPII-2024SolutionsCopyranaabhiruchiNo ratings yet
- 03 NOC H BONDDocument38 pages03 NOC H BONDmyviralshow2024No ratings yet
- Oxidaciones_alcoholesDocument11 pagesOxidaciones_alcoholesalbertiiyo19No ratings yet
- L6 Reactions of Carboxylic Acid DerivativesDocument21 pagesL6 Reactions of Carboxylic Acid DerivativesCheng FuNo ratings yet
- Turuan As. karboksilatKOL A #2Document24 pagesTuruan As. karboksilatKOL A #2Mahendra AdityaNo ratings yet
- Preparation of Carboxylic Acid and Their DerivativesDocument7 pagesPreparation of Carboxylic Acid and Their DerivativesYuni PurnamasariNo ratings yet
- Ketones and Aldehydes: Organic ChemistryDocument56 pagesKetones and Aldehydes: Organic ChemistryHezron BumbunganNo ratings yet
- Acids Derivatives 2021Document59 pagesAcids Derivatives 2021chennivoon00No ratings yet
- A, K&CDocument45 pagesA, K&CDayallini Winx100% (1)
- AlcoholsDocument91 pagesAlcoholsWAN NUR AISYAH WAN AZIZANNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Ii CHM 301: (Chapter 4)Document14 pagesOrganic Chemistry Ii CHM 301: (Chapter 4)WAN NUR AISYAH WAN AZIZANNo ratings yet
- Organic CH Emistry Ii CHM301: Carboxylic AcidsDocument53 pagesOrganic CH Emistry Ii CHM301: Carboxylic AcidsWAN NUR AISYAH WAN AZIZANNo ratings yet
- Carbonyl GroupDocument92 pagesCarbonyl GroupWAN NUR AISYAH WAN AZIZANNo ratings yet
- ELECTRONIC COMPONENTS HandoutDocument22 pagesELECTRONIC COMPONENTS HandoutVineeth WilsonNo ratings yet
- Solar CableDocument12 pagesSolar CableNitesh MehtaNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Information Communication Technology (Ict)Document27 pagesUnit 6 Information Communication Technology (Ict)Christine Joy MarananNo ratings yet
- Diagrama Electrónico Adv8105Document30 pagesDiagrama Electrónico Adv8105Fast ServiceNo ratings yet
- Entry Load and Exit Load: What Are Exit Loads in Mutual Funds?Document22 pagesEntry Load and Exit Load: What Are Exit Loads in Mutual Funds?Zea ZakeNo ratings yet
- Get The Affect Theory of Silvan Tomkins for Psychoanalysis and Psychotherapy Recasting the Essentials 1st Edition E. Virginia Demos PDF ebook with Full Chapters NowDocument81 pagesGet The Affect Theory of Silvan Tomkins for Psychoanalysis and Psychotherapy Recasting the Essentials 1st Edition E. Virginia Demos PDF ebook with Full Chapters Nowordascutri8u100% (1)
- Generation Stair Tower User Guide 2016 FVDocument32 pagesGeneration Stair Tower User Guide 2016 FVpaisley510No ratings yet
- Goodridge Catalogue Performance PartsDocument92 pagesGoodridge Catalogue Performance PartsDLTNo ratings yet
- Skinless Longanisa I. ObjectivesDocument3 pagesSkinless Longanisa I. ObjectivesJustclick CompNo ratings yet
- Application of MemsDocument7 pagesApplication of MemsAnuja SuryanNo ratings yet
- CH 17Document24 pagesCH 17Ameer ElatmaNo ratings yet
- 8656 Assignment No 1Document16 pages8656 Assignment No 1Muhammad SaleemNo ratings yet
- BEST-2K Method For Characterizing Dual-PermeabilitDocument20 pagesBEST-2K Method For Characterizing Dual-PermeabilitchetanNo ratings yet
- Haixiong Ye T D CONDocument21 pagesHaixiong Ye T D CONvijayakumareeeNo ratings yet
- KS3 Energy Transfer 1Document92 pagesKS3 Energy Transfer 1Dominic Wynes-DevlinNo ratings yet
- Modern Wound Dressing - pptx-1Document32 pagesModern Wound Dressing - pptx-1puvi.mayor2104No ratings yet
- 7.sınıf Ingilizce 2.dönem 1.yazılısı-2Document2 pages7.sınıf Ingilizce 2.dönem 1.yazılısı-2hazan.mamacitaNo ratings yet
- Short Notes For Spotting The Errors Questions PDFDocument2 pagesShort Notes For Spotting The Errors Questions PDFVivek PatelNo ratings yet
- PMSBY Cons-Cum-Decl Orm - 10062021Document2 pagesPMSBY Cons-Cum-Decl Orm - 10062021subrahmanyamNo ratings yet
- Test de Ingles 6 PDF 2Document1 pageTest de Ingles 6 PDF 2daniela ijajiNo ratings yet
- De La Salle University Gokongwei College of Engineering Civil Engineering DepartmentDocument9 pagesDe La Salle University Gokongwei College of Engineering Civil Engineering DepartmentAdrian PerezNo ratings yet
- Review Questions EssayDocument3 pagesReview Questions EssayJ Alexander VernonNo ratings yet
- Standard Iiec SyllabusDocument19 pagesStandard Iiec SyllabusChairman IIEC InstituteNo ratings yet
- 2018 Modul Biologi Kem Straight A+Document29 pages2018 Modul Biologi Kem Straight A+SMK SERI NERING PPD BESUTNo ratings yet
- Fivaxyouth BookletDocument14 pagesFivaxyouth BookletJG DEVETINo ratings yet
- C1000-154 STU C1000154v2STUSGC1000154Document10 pagesC1000-154 STU C1000154v2STUSGC1000154Gisele SouzaNo ratings yet
- 14 - JSA For Replacement of Tube Bundles of (100-EA4-C3, C8) & 284-E52 & 810E7 With New OneDocument1 page14 - JSA For Replacement of Tube Bundles of (100-EA4-C3, C8) & 284-E52 & 810E7 With New OneSHAH NAWAZ SAEEDNo ratings yet
- GlomerulonephritisDocument1 pageGlomerulonephritisteena6506763No ratings yet
- 12.07.20. O&M Manual 41013 - New PLCDocument41 pages12.07.20. O&M Manual 41013 - New PLCFranco Sebastián Genre100% (1)