Assessment of the Reproductive
System
MRS. LUCY MENG’ANYI
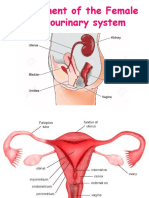
Female Reproductive System
• External genitalia—vulva, labia majora, mons
pubis, labia minora, clitoris, vestibule,
perineum
• Internal genitalia—vagina, uterus, corpus,
cervix, fallopian tubes, ovaries
• Breasts
• Menstruation and menopause
Internal Female Genitalia
Female Breast
Male Reproductive System
• External genitalia—penis, scrotum
• Internal genitalia—testes and prostate gland
• Inguinal area
Internal Male Genitalia
Assessment Techniques: Female
• History: pain, bleeding, discharge, masses
• Physical assessment
– Breast examination
– Abdominal examination
– Examination of the external genitalia
– Pelvic examination
– Bimanual examination
– Rectovaginal examination
Assessment techniques
History
• The nurse uses data about client’s age, sex,
and culture to assess the risk for certain
diseases. The nurse considers the client’s age
in evaluating the reproductive system.
• Personal history( the nurse assesses the
client’s health habits, such as diet, sleep, and
exercise patterns.)
• Family history helps to determine the client’s
risk for conditions that affects reproductive
system functioning.
• Diet history is often critical for the correct
interpretation of presenting symptoms of the
reproductive system.
• Social history of the client provides insight into
the whole person, including stressors, job
history, education.
Obstetric History
• Number of pregnancies, live
deliveries, stillbirths,
abortions
• Difficulties with
pregnancies, deliveries
• Birth weight of babies
• Problems with infertility
Use of Contraception
• Type used (past and
present)
• Difficulties with
method, suitability
• If discontinued, reasons
for doing so
Sexual History
• Sexual orientation
• Regularity of intercourse
• Number of partners in the
past 12 months
• Associated symptoms (e.g.,
pain, postcoital bleeding)
• Sexual dysfunction
Current health problem
• If a client seeks medical attention for a
problem related to the reproductive
system, the nurse asks additional
questions to explore the chief complaint.
1. Onset (sudden or gradual)
2. Chronology
3. Current situation (improving or deteriorating)
4. Location
5. Radiation
6. Quality
7. Timing (frequency, duration)
8. Severity
9. Precipitating and aggravating factors
10. Relieving factors
11. Associated symptoms
12. Effects on daily activities
13. Previous diagnosis of similar episodes
14. Previous treatments
15. Efficacy of previous treatments
Most complaints concern:
• Pain,
• Discharge
• Masses and
• Reproductive functioning
Pain
• Onset, location, radiation, character, severity
• Relation to menstruation
• Aggravating and relieving factors
• Use of analgesics and their effect
• Associated gastrointestinal, urinary or vaginal
symptoms
• Are symptoms related to an encounter with a
new sexual partner?
• The nurse should not assume that the initial
medical diagnosis is conclusive
Vaginal Discharge
The nurse asks about:
• Onset, color, odor, consistency, quantity
• Relation to menstrual period
• Associated symptoms (e.g., rectal or urethral discharge,
vaginal itch or burning, urinary symptoms, malaise, abdominal
pain, fever)
• Relation to medication use (e.g., antibiotics, steroids)
• History of previous vaginal or pelvic infections and their
treatment
Masses
N/B: Any reported masses in
the breast should be evaluated
for:
• Soreness, tenderness and
their relation to menstrual
cycle
• Redness, swelling, nipple
discharge
• Change in contour, presence
of masses
• Is client breast-feeding?
Bleeding
• Heavy bleeding or lack of bleeding may concern the
woman.
• The possibility of pregnancy is considered in any
sexually active woman with amenorrhea. Any
postmenopausal bleeding needs to be evaluated.
• The nurse asks when the bleeding occurs in relation
to certain events, such as the menstrual cycle or
menopause, intercourse, trauma. In addition, the
nurse notes the presence of associated symptoms
Other Associated Symptoms
• Ulcerations
• Persistent lesions
• Sense of pelvic relaxation (pelvic organs feel as
though they are falling down or out)
• Infertility
• Pelvic infection
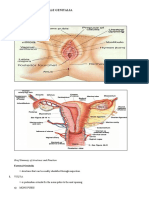
Bimanual Pelvic Examination
Breast
•Teach client on Breast Self-Exam
• done monthly
• 7-10 days from the first day
of your period
•Same day every month if you
are not menstruating
Click on the Homepage link on the left to exit
Stand in front of a mirror and look at each breast
separately. Note the size, shape, symmetry
Normal – symmetrical (may be slightly symmetrical, color
consistent with body, no lesion, edema, dimpling, retraction
Nipple and areola – note color, shape, symmetry, inversion,
eversion, discharge, masses, lesions
Change in nipple from everted to inverted or in the
direction in which is pointing - underlying mass
Discharge not associated with pregnancy or
breastfeeding be evaluated further – obtain specimen –
R/O – infection, hormonal factors, cancer
Click on the Homepage link on the left to exit
Raise arms over head and inspect
breasts, as turns slowly from side to
side. Assess axilla too – color, masses,
lesions, hair distribution
Click on the Homepage link on the left to exit
Press hands on hips and push
shoulders forward. Look at each
breast separately.
Click on the Homepage link on the left to exit
Stand in front of a mirror and start BSE just below the collar bone.
Use the 3 middle fingertips of your left hand. Methods: vertical strip, pie
wedge or concentric circles
•Apply firm pressure as you go back or forth in a pattern covering all
the breast area including the nipple.
•Extend the examination to the breast tissue in the underarm
Note texture, consistency, tenderness, masses – normally nontender
(premenstrual may be tender and nodular), no masses or lesion
Lie down and raise one arm above head. Examine breasts as
before, omitting the underarm.
Palpate nipples for surface characteristics and discharge by
gently decompressing nipple between index finger and thumb
Click on the Homepage link on the left to exit
Male Breast examination
• Inspect breast, client seated – color,
symmetry, skin lesions, enlargement
– Normal – flat without rashes or lesions or
enlargement.
– Overweight men may have thicker fatty layer of
tissue on the chest giving apperance of breast
enlargement
• But if reports sudden enlargement or associated
tenderness, further evaluation needed
– Areola mass and nipple – intact, smooth, and of
equal color, size, shape bilaterally
• Palpate breasts – client seated. Normal –
tissue smooth, intact, nontender, no unilateral
tenderness or masses
• Palpate nipples – normally no discharge
• Palpate axilla – no lymphatic enlargement or
tenderness
Physical Exam
Preparation
Lithotomy position and
draping
Measures to enhance
comfort during exam
Slide 26-30
Objective Data—Physical Exam
(cont.)
Equipment
Gloves
Protective clothing for examiner
Goose-necked lamp with a strong light
Vaginal speculum of appropriate size
Large cotton-tipped applicators (rectal swabs)
Materials for cytologic study
Lubricant
Vaginal speculum
Objective Data—Physical Exam
(cont.)
External genitalia— Inspection
Skin color
Hair distribution
Labia majora
Any lesions
Clitoris
Labia minora
Urethral opening
Vaginal opening
Perineum
Anus
Objective Data—Physical Exam
(cont.)
External genitalia—Palpation
Skene’s glands
Bartholin’s glands
Support of pelvic musculature
Slide 26-34
Objective Data—Physical Exam
(cont.)
Internal genitalia—
Speculum examination
Insertion technique
Cervix and os
Color
Position
Size
Os
Surface
Any Nabothian cysts
Cervical secretions
Objective Data—Physical Exam
(cont.)
Obtain cervical smears and cultures
Vaginal pool
Cervical scrape
Endocervical specimen
Data to include for the
laboratory
Inspect vaginal wall
Objective Data—Physical Exam
(cont.)
Internal genitalia—Bimanual Examination
Palpation technique Adnexa
Cervix Rectovaginal
Consistency examination
Contour Rectovaginal septum
Mobility Posterior uterine wall
Uterus Cul-de-sac
Rectum
Results
The external genitals do not have Abnor- Sores or rough, raised spots on
sores or other abnormal growths mal
the skin (such as genital warts)
(such as genital warts).
may be seen on the external
genitals. Redness and itching of
the labia may indicate irritation
The vaginal walls are reddish pink (from feminine products or sexual
and contain slight folds or ridges. activity) or infection (such as
No sores or growths are seen genital herpes or another sexually
transmitted disease).
The cervix is moist and looks like
small, rounded "doughnut" with a
Vaginal discharge that has an
hole or slit in the center. It may
unpleasant odor may indicate an
appear pinkish, bluish, or pale.
infection. Discharge that looks
curdy (like cottage cheese)
vaginal yeast infection.
Any discharge should be clear
and thin or white and creamy.
The discharge should not have an Redness of the cervix may be a
unpleasant odor, contain blood, or sign of inflammation (cervicitis)
appear curdy. or an infection.
Images of Genital warts
Assessment Techniques: Male
• Examination of the external genitalia
• Examination for inguinal hernia
• Examination of the rectum and prostate
Subjective Data—Health History
Questions
• Symptoms – pain, lesions, swelling, discharge,
• genitourinary symptoms - Frequency, urgency, and
nocturia, Dysuria, Hesitancy and straining, Urine color
• Sexual history - Sexual activity and contraceptive use
• Penis—pain, lesion, and/or discharge
• Scrotum—self-care behaviors; lump
• Sexually transmitted disease contact
Objective Data—The Physical Exam
• Preparation
Position
Apprehension regarding exam
• Equipment needed
Gloves
Occasionally need
• Glass slide for urethral specimen
• Materials for cytology
• Flashlight
Objective Data—The Physical Exam
(cont.)
• Penis—Inspect and palpate
• Skin
• Glans
• Urethral meatus
• Pubic hair
• Urethral discharge
• Shaft
Objective Data—The Physical Exam
(cont.)
• Scrotum—Inspect and palpate
• Skin
• Testis
• Epididymis
• Spermatic cord
• Any mass
• Prostate – shape and size of walnut, smooth,
rubbery, nontender
Note characteristics
Genital self-exam
Teach - 14 years and older, a monthly exam be
done.
Penis – check for swelling, sores, blisters,
discharge. Palpate entire shaft from base to
tip to check for lumps, tenderness, swelling
Testicular exam – best done after a warm bath
or shower – relaxes scrotum
• Stand in front of mirror if possible – check for
swelling on scrotal skin
• Examine each testicle with both hands
– Place index and middle fingers under the testicle with
thumbs placed on top
– Roll testicles gently between the thumbs and fingers
– note size, shape, consistency, masses, nodules,
tenderness of testes
– Normal – scrotal skin rough without lesions. Testes
rubbery, round, movable, smooth, 2cm× 5cm in size,
no pain (may be slight tenderness with compression)
– Abnormal – Mass, testicle enlarged, retracted,
painful, one or both tested undescended
• Palpate ducts and inguinal lymphnodes – normal:
no swelling or nodules, no palpable nodes
Objective Data—The Physical Exam (cont.)
• Check for hernia—Inspect
and palpate
Person standing and
straining down
Palpation technique
• Inguinal lymph nodes
• Teach testicular self-
examination
T = Timing
S = Shower
E = Examination points