Programming Language Swift Overview
- 2. Swift
- 3. What's Swift
- 4. What's Swift
- 5. Variables // variable var name: String = "John Doe" var temperature: Double = 36.5 var year: Int = 2014 var visible: Bool = true ! year = 2015
- 6. Type Inference // variable var name: String = "John Doe" var temperature: Double = 36.5 var year: Int = 2014 var visible: Bool = true ! name = "Steve Jobs" // OK temperature = 36.8 // OK year = 2015 // OK visible = false // OK
- 7. Type Inference // variable var name: String = "John Doe" var temperature: Double = 36.5 var year: Int = 2014 var visible: Bool = true ! name = "Steve Jobs" // OK temperature = 36.8 // OK year = 2015 // OK visible = false // OK
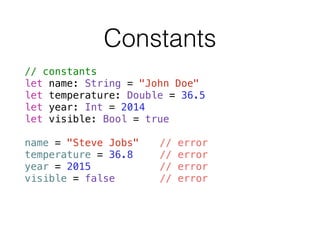
- 8. Constants // constants let name: String = "John Doe" let temperature: Double = 36.5 let year: Int = 2014 let visible: Bool = true ! name = "Steve Jobs" // error temperature = 36.8 // error year = 2015 // error visible = false // error
- 9. Unicode Names let 🐶: Character = "🐶" let 🐮: String = "🐮" let dog: Character = "dog" // error let cow: String = "cow" let π = 3.1415927 let 言語 = "Japanese"
- 10. String Operation let hello = "Hello" let world = "World" let greeting = hello + " " + world // "Hello World" ! let a = 3, b = 5 let result = "(a) + (b) = (a + b)" // "3 + 5 = 8"
- 11. Array and Dictionary Literals // Mixed Object Type Array var array = ["Tokyo", 3, true] ! // Typed Collection var list1: String[] = ["Ja", "En", "Fr"] var list2: String[] = ["Ja", "En", 2.0] //NG ! // Dictionary var legs = ["cat":4, "snake":0, "dog":2]
- 12. Array Access // declaration var items = ["Ja", "En", "Fr"] ! // accessors let item = items[1] // "En" items.insert("De", atIndex: 0) // De,Ja, … items.append("It") // De,Ja,En,Fr,It items.removeAtIndex(1) // De,En,Fr,It items.removeLast() // De,En,Fr
- 13. Array Access var names = ["Robert", "Ken"] ! // append names += "Joe" names += ["Mike", "Paul"] ! // replace names[0] = "Bob" names[2..4] = ["Jim", "Alex", "Bill"] // Bob,Ken,Jim,Alex,Bill,Paul
- 14. Dictionary var dict = ["Ja":"Japanese", "En":"English", "Fr":"French"] ! // read access let lang = dict["Ja"] // "Japanese" ! // write access dict["De"] = "German" dict["Ja"] = nil
- 15. Tuple let rgb = (128, 255, 0) let result = (404, "Not Found") let item = (2, "banana", 0.75) ! let r = rgb.0 // 128 let code = result.0 // 404 let name = item.1 // "banana"
- 16. // non optional var str1: String = nil // error: non-opt var str2: String = "" // OK var num1: Int = nil // error: non-opt var num2: Int = 496 // OK ! // optional var str3: String? = nil // OK: optional var num3: Int? = nil // OK: optional Optional & Non Optional
- 17. If Statement ! if items.count > 0 { // OK: some code here } ! if (items.count > 0) { // OK: parentheses are optional } ! // error (requires curly brace) if (items.count > 0) println("")
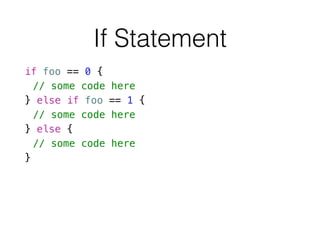
- 18. If Statement if foo == 0 { // some code here } else if foo == 1 { // some code here } else { // some code here }
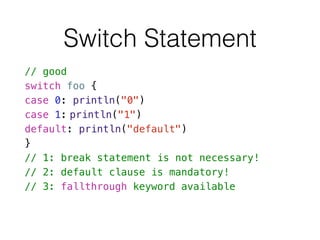
- 19. Switch Statement // good switch foo { case 0: println("0") case 1: println("1") default: println("default") } // 1: break statement is not necessary! // 2: default clause is mandatory! // 3: fallthrough keyword available
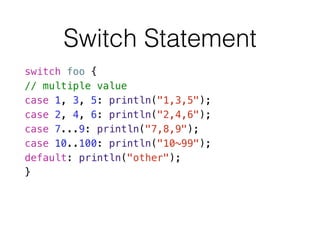
- 20. Switch Statement switch foo { // multiple value case 1, 3, 5: println("1,3,5"); case 2, 4, 6: println("2,4,6"); case 7...9: println("7,8,9"); case 10..100: println("10~99"); default: println("other"); }
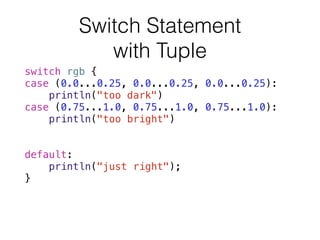
- 21. Switch Statement with Tuple switch rgb { case (0.0...0.25, 0.0...0.25, 0.0...0.25): println("too dark") case (0.75...1.0, 0.75...1.0, 0.75...1.0): println("too bright") case let (r, g, b) where r==g && g==b: println("quite grey") default: println("just right"); }
- 22. switch rgb { case (0.0...0.25, 0.0...0.25, 0.0...0.25): println("too dark") case (0.75...1.0, 0.75...1.0, 0.75...1.0): println("too bright") case let (r, g, b) where r==g && g==b: println("quite grey") default: println("just right"); } Switch Statement with where clause
- 23. Loops // while loop while !done { /*code*/ } ! // do while loop do { /*code*/ } while !done ! // for loop for var i = 0 ; i < 100 ; ++i { /*code*/ }
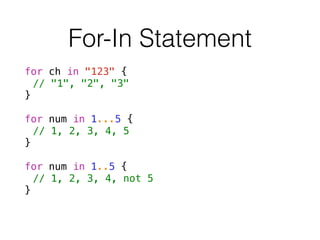
- 24. For-In Statement for ch in "123" { // "1", "2", "3" } ! for num in 1...5 { // 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 } ! for num in 1..5 { // 1, 2, 3, 4, not 5 }
- 25. For-In // array for item in ["En", "Ja", "Fr"] { // "En", "Ja", "Fr" } // dictionary var items = ["Ja":"Japanese","En":"English"] for (code, name) in items { println("(code): (name)") }
- 26. Functions // no parameter func foo() { … } // with parameter func bar(name: String) { … } // with default parameter func buz(name: String = "World") { … } ! foo() bar("Tokyo") buz()
- 27. Functions with Returning Values func foo() -> String { return "foo" } func bar() -> String? { return nil; } func buz() -> (Int, String) { return (404, "Not Found") }
- 28. Optional Return Type func indexOfString(string: String, array: String[]) -> Int { for (index, value) in enumerate(array) { return index; } return nil; // error: non optional }
- 29. Optional Return Type func indexOfString(string: String, array: String[]) -> Int? { for (index, value) in enumerate(array) { return index; } return nil; // OK: optional }
- 30. Optional Parameters func foo(name: String) { } ! func bar(name: String?) { } ! foo("Ken") // OK foo(nil) // NG: not optional bar("Ken") // OK bar(nil) // OK: optional
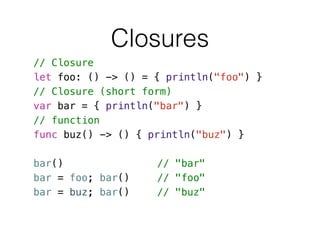
- 31. Closures // Closure let foo: () -> () = { println("foo") } // Closure (short form) var bar = { println("bar") } // function func buz() -> () { println("buz") } ! bar() // "bar" bar = foo; bar() // "foo" bar = buz; bar() // "buz"
- 32. class Shape { var center:CGPoint; init(center:CGPoint) { self.center = center; } } class Circle : Shape { var radius: Double; init(center:CGPoint, radius:Double) { self.radius = radius; super.init(center: center) } } Classes
- 33. class Counter { var value: Int = 0 init() { } func increment() { value++ } } ! var counter = Counter() // no alloc counter.increment() println(counter.value) // 1 Properties and Methods
- 34. class Range { var location, length: Double; init(location:Double, length:Double) { self.location = location; self.length = length; } var mid: Double { get { return location + length/2.0; } set { location = newValue - length/2.0; } } // if no setter then readonly property } Getter & Setter
- 35. class Ship { var health: Double } ! class Car : Mammal { override var description: String { return super.description + ".Ape" } } Overriding Properties
- 36. class User { var name: String = ""; } ! class Admin : User { override var name: String { willSet { println("(newValue)"); } didSet { println("(oldValue)"); } } } Property Observers
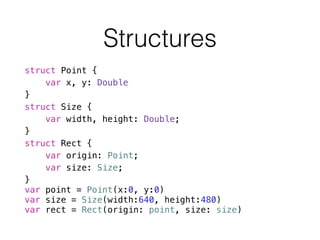
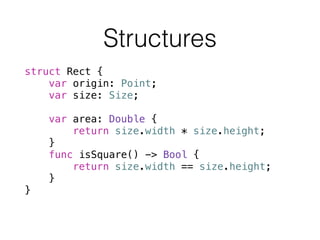
- 37. struct Point { var x, y: Double } struct Size { var width, height: Double; } struct Rect { var origin: Point; var size: Size; } var point = Point(x:0, y:0) var size = Size(width:640, height:480) var rect = Rect(origin: point, size: size) Structures
- 38. struct Rect { var origin: Point; var size: Size; ! var area: Double { return size.width * size.height; } func isSquare() -> Bool { return size.width == size.height; } } Structures
- 39. Classes & Structures • Classes • instances are passed by reference • subclassing ! • Structures • instances are passed by value • no subclassing
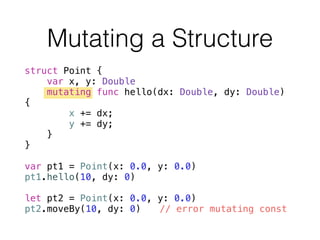
- 40. struct Point { var x, y: Double mutating func hello(dx: Double, dy: Double) { x += dx; y += dy; } } ! var pt1 = Point(x: 0.0, y: 0.0) pt1.hello(10, dy: 0) ! let pt2 = Point(x: 0.0, y: 0.0) pt2.moveBy(10, dy: 0) // error mutating const Mutating a Structure
- 41. enum enum Direction { case Left, Right init() { self = .Left; } var description: String { switch self { case .Left: return "Left" case .Right: return "Right" } } } var direction1 = Direction.Left; direction1 = .Right; var direction2 = Direction() println(direction1.description)
- 42. enum Direction { case Left, Right init() { self = .Left; } var description: String { switch self { case .Left: return "Left" case .Right: return "Right" } } } var direction1 = Direction.Left; direction1 = .Right; var direction2 = Direction() println(direction1.description) enum
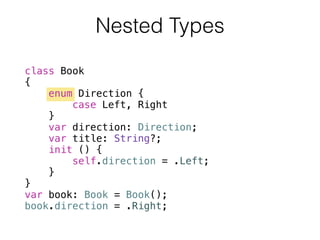
- 43. Nested Types class Book { enum Direction { case Left, Right } var direction: Direction; var title: String?; init () { self.direction = .Left; } } var book: Book = Book(); book.direction = .Right;
- 44. Extensions extension Size { mutating func scaleBy(scale: Double) { width *= scale height *= scale } } ! var size = Size(width: 100, height: 100); size.scaleBy(2.0)
- 45. Extensions extension Int { func repetitions(task: () -> ()) { for i in 0..self { task() } } } ! 32.repetitions({ println("Hello") })
- 46. Extension extension Double { var km: Double { return self * 1_000.0 } var m: Double { return self } var cm: Double { return self / 100.0 } var mm: Double { return self / 1_000.0 } var ft: Double { return self / 3.28084 } } ! let marathon = 42.km + 195.m // 42,195.0
- 47. Generic struct Stack<T> { var elements = T[]() mutating func push(element: T) { elements.append(element) } mutating func pop() -> T { return elements.removeLast() } } var stack1 = Stack<Int>() var stack2 = Stack<Point>() var stack3 = Stack<Rect>()
- 48. Generic var dic1: Dictionary = Dictionary<String, String>() ! var dic2: Dictionary = Dictionary<String, Int>() ! var dic3: Dictionary = Dictionary<String, AnyObject>()
- 49. Anonymous for (key, _) in dictionary { println(key) } ! let (red, green, blue, _) = color.rgba;
- 50. Protocols protocol Countable { var count : Int { get }; func increment(); } ! class PageCounter : Countable { var count : Int = 0; func increment() { count++; } }
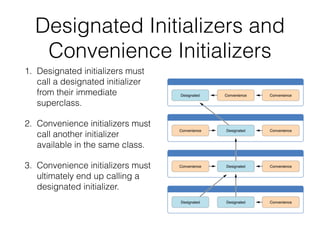
- 51. Designated Initializers and Convenience Initializers 1. Designated initializers must call a designated initializer from their immediate superclass. 2. Convenience initializers must call another initializer available in the same class. 3. Convenience initializers must ultimately end up calling a designated initializer.
- 52. Deinitialization class SomeObject { var fileHandle: NSFileHandle? init(path: String) { var fileURL = NSURL.fileURLWithPath(path); var error: NSError? = nil; fileHandle = NSFileHandle. fileHandleForReadingFromURL(fileURL, error: &error) } func parse() -> AnyObject? { // ... return nil } deinit { fileHandle?.closeFile() } }
- 53. Shorthand External Parameter Names func stringFromInt(#value:Int) -> String { return "(value)" } func stringFromDouble(value:Double) -> String { return "(value)" } var a = stringFromInt(value:256); // OK var b = stringFromInt(256); // NG var c = stringFromDouble(value:256.3); // NG var d = stringFromDouble(256); // OK
- 54. Variadic Parameters func total(numbers: Int...) -> Int { var total: Int = 0; for number in numbers { total += number; } return total; } ! let sum = total(1, 2, 3, 4, 5)
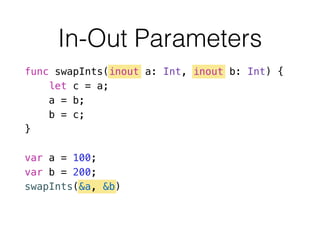
- 55. In-Out Parameters func swapInts(inout a: Int, inout b: Int) { let c = a; a = b; b = c; } ! var a = 100; var b = 200; swapInts(&a, &b)
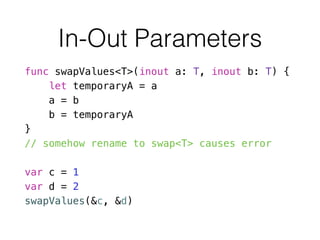
- 56. In-Out Parameters func swapValues<T>(inout a: T, inout b: T) { let temporaryA = a a = b b = temporaryA } // somehow rename to swap<T> causes error ! var c = 1 var d = 2 swapValues(&c, &d)
- 57. Typealias typealias AudioSample = UInt16
- 58. Labeled Statements var strings: String[] = ["Hello World", "This is a pen", "Wow!"] ! label: for string in strings { for ch in string { if (ch == "!") { break label; } } }
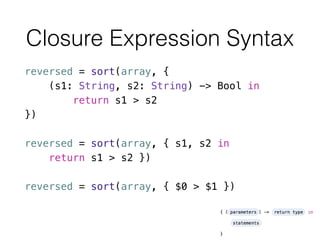
- 59. Closure Expression Syntax reversed = sort(array, { (s1: String, s2: String) -> Bool in return s1 > s2 }) ! reversed = sort(array, { s1, s2 in return s1 > s2 }) ! reversed = sort(array, { $0 > $1 })
- 60. Lazy Stored Properties class BookManager { init() { println("BookManager") } } class Book { @lazy var manager = BookManager() init() { println("Book") } } var book = Book() book.manager
- 61. Subscript Syntax class Paragraphs { var strings = String[](); // ... subscript(index: Int) -> String { get { return strings[index] } set { strings[index] = newValue } } }
- 62. Identity Operators • Identity Operators • bridgeToObjectiveC
- 63. Downcasting for object in objects { let view = object as UIView view.hidden = true } ! for view in objects as UIView[] { view.hidden = true }
- 64. Type Evaluation for thing in things { switch thing { case 0 as Int: println("0 as Int") case 0 as Double: println("0 as Double") case let value as Int: println("Int") case let value as Double where value > 0: println("Double value > 0") case is Double: println("Double") case let string as String: println("") case let (x, y) as (Double, Double): println("(x),(y)") case let v as Vector2D: println("Vector2D") default: println("other") } }
- 65. operator struct Vector2D { var x = 0.0, y = 0.0 } ! @infix func + (lhs: Vector2D, rhs: Vector2D) -> Vector2D { return Vector2D(x: lhs.x + rhs.x, y: lhs.y + rhs.y) } ! var v1 = Vector2D(x:10, y:20) var v2 = v1 + Vector2D(x:3, y:4) Note: @prefix @infix @postfix
- 67. @synchronized Left Intentionally Blank ! Why not using NSLock?
- 68. Key Value Observer class Car : NSObject { var speed : Double = 0.0 override var description : String { return "car: speed=(speed)" } } class Dashboard : NSObject { var car : Car; init(car: Car) { self.car = car; super.init(); car.addObserver(self, forKeyPath: "speed", options: .New, context: nil) } override func observeValueForKeyPath(keyPath: String!, ofObject: AnyObject!, change: NSDictionary!, context: CMutableVoidPointer) { if keyPath == "speed" { println(ofObject.description) } } } var car = Car() var dashboard = Dashboard(car:car) car.speed = 2
- 69. Class Method class Foo { // class var bar: Int = 0; class func classMethod() { } } ! var foo = Foo() foo.dynamicType.classMethod()
- 70. Thank you










![Array and Dictionary Literals
// Mixed Object Type Array
var array = ["Tokyo", 3, true]
!
// Typed Collection
var list1: String[] = ["Ja", "En", "Fr"]
var list2: String[] = ["Ja", "En", 2.0] //NG
!
// Dictionary
var legs = ["cat":4, "snake":0, "dog":2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/swift-1406-140614231948-phpapp01/85/Programming-Language-Swift-Overview-11-320.jpg)
![Array Access
// declaration
var items = ["Ja", "En", "Fr"]
!
// accessors
let item = items[1] // "En"
items.insert("De", atIndex: 0) // De,Ja, …
items.append("It") // De,Ja,En,Fr,It
items.removeAtIndex(1) // De,En,Fr,It
items.removeLast() // De,En,Fr](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/swift-1406-140614231948-phpapp01/85/Programming-Language-Swift-Overview-12-320.jpg)
![Array Access
var names = ["Robert", "Ken"]
!
// append
names += "Joe"
names += ["Mike", "Paul"]
!
// replace
names[0] = "Bob"
names[2..4] = ["Jim", "Alex", "Bill"]
// Bob,Ken,Jim,Alex,Bill,Paul](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/swift-1406-140614231948-phpapp01/85/Programming-Language-Swift-Overview-13-320.jpg)
![Dictionary
var dict = ["Ja":"Japanese", "En":"English",
"Fr":"French"]
!
// read access
let lang = dict["Ja"] // "Japanese"
!
// write access
dict["De"] = "German"
dict["Ja"] = nil](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/swift-1406-140614231948-phpapp01/85/Programming-Language-Swift-Overview-14-320.jpg)





![For-In
// array
for item in ["En", "Ja", "Fr"] {
// "En", "Ja", "Fr"
}
// dictionary
var items = ["Ja":"Japanese","En":"English"]
for (code, name) in items {
println("(code): (name)")
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/swift-1406-140614231948-phpapp01/85/Programming-Language-Swift-Overview-25-320.jpg)


![Optional Return Type
func indexOfString(string: String,
array: String[]) -> Int {
for (index, value) in enumerate(array) {
return index;
}
return nil; // error: non optional
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/swift-1406-140614231948-phpapp01/85/Programming-Language-Swift-Overview-28-320.jpg)
![Optional Return Type
func indexOfString(string: String,
array: String[]) -> Int? {
for (index, value) in enumerate(array) {
return index;
}
return nil; // OK: optional
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/swift-1406-140614231948-phpapp01/85/Programming-Language-Swift-Overview-29-320.jpg)












![Generic
struct Stack<T> {
var elements = T[]()
mutating func push(element: T) {
elements.append(element)
}
mutating func pop() -> T {
return elements.removeLast()
}
}
var stack1 = Stack<Int>()
var stack2 = Stack<Point>()
var stack3 = Stack<Rect>()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/swift-1406-140614231948-phpapp01/85/Programming-Language-Swift-Overview-47-320.jpg)







![Labeled Statements
var strings: String[] =
["Hello World", "This is a pen", "Wow!"]
!
label: for string in strings {
for ch in string {
if (ch == "!") {
break label;
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/swift-1406-140614231948-phpapp01/85/Programming-Language-Swift-Overview-58-320.jpg)

![Subscript Syntax
class Paragraphs {
var strings = String[]();
// ...
subscript(index: Int) -> String {
get {
return strings[index]
}
set {
strings[index] = newValue
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/swift-1406-140614231948-phpapp01/85/Programming-Language-Swift-Overview-61-320.jpg)

![Downcasting
for object in objects {
let view = object as UIView
view.hidden = true
}
!
for view in objects as UIView[] {
view.hidden = true
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/swift-1406-140614231948-phpapp01/85/Programming-Language-Swift-Overview-63-320.jpg)






