Sentiment Analysis using Python
With this Machine Learning Project, we will be doing sentiment analysis of hotel reviews made by the customers of the hotel. Sentiment Analysis is done to know about the sentiments of the people. Sentiment Analysis is a technique used in data science to analyze the data and to take steps based on the analysis to improve the business.
So, you see that sentiment analysis is very important.
Sentiment Analysis
In sentiment analysis, we analyze the reviews given by the customers or people and analyze whether the customer is satisfied with the product or not. This is a very important analysis in the business world to improve the business. Sentiment Analysis can be done in any business field which are providing services.
For example- In this machine learning project, we are going to do the sentiment analysis of hotel reviews given by the customers and analyze whether the customer is happy with the product or not.
Why do we need to build a Machine Learning model for it?
Because we know, that a hotel has a lot of visitors so the number of reviews given by the customers is very high. It is not possible to see all the reviews by single persons. So, it is very necessary that we have a machine learning model that will do this task for us.
Count Vectorizer
This is a very important thing that we will be using in this project. Count Vectorizer is a tool that will help us to work with the text. As we can’t apply SVM on a text directly, so we need to use this function. It helps to convert the text into a vector on the basis of the frequency count.
Count Vectorizer creates a matrix which different words as the columns. The rows are equal to the number of sentences in the dataset. The value of each cell in this matrix is nothing but equal to the count of the word of a particular column in the sentence corresponding to a particular row.
Using this function, we will convert the reviews written in text form into vectors by using the CountVectorizer function, and then we can use SVM on it.
The Model Architecture
The model we are using in this project is an SVM classifier with Count Vectorisation. SVM is termed as Support Vector Machines. SVM is one of the most popular methods in machine learning for classification problems.
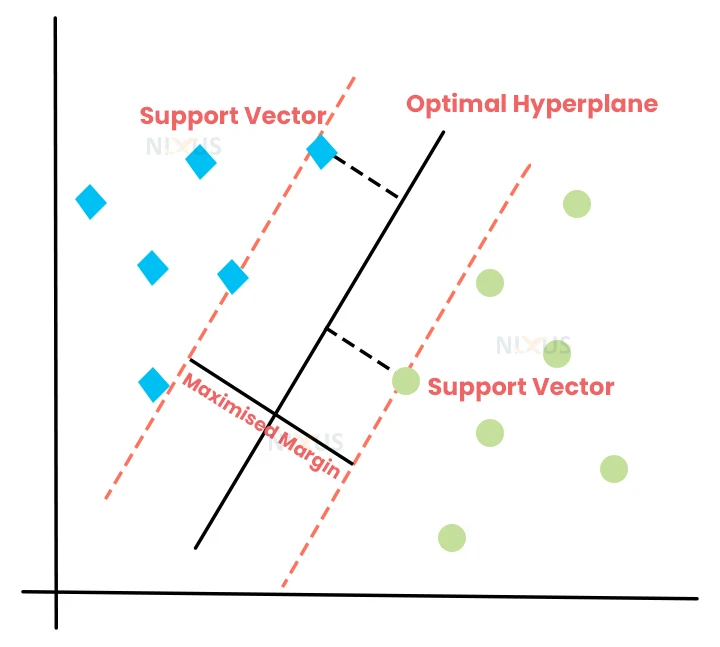
SVM work in a way that it tries to draw a hyperplane in an n-dimensional space such that it can maximize the space between points. These points are nothing but called support vectors. Hence the name is termed Support Vector Machines.
Look at the picture above. This picture clearly shows us how support vectors work. The hyperplane is created in such a way that it tries to maximize the distance between green and blue vectors. The distance between vectors and the hyperplane is known as the margin.
There are two types of SVM:
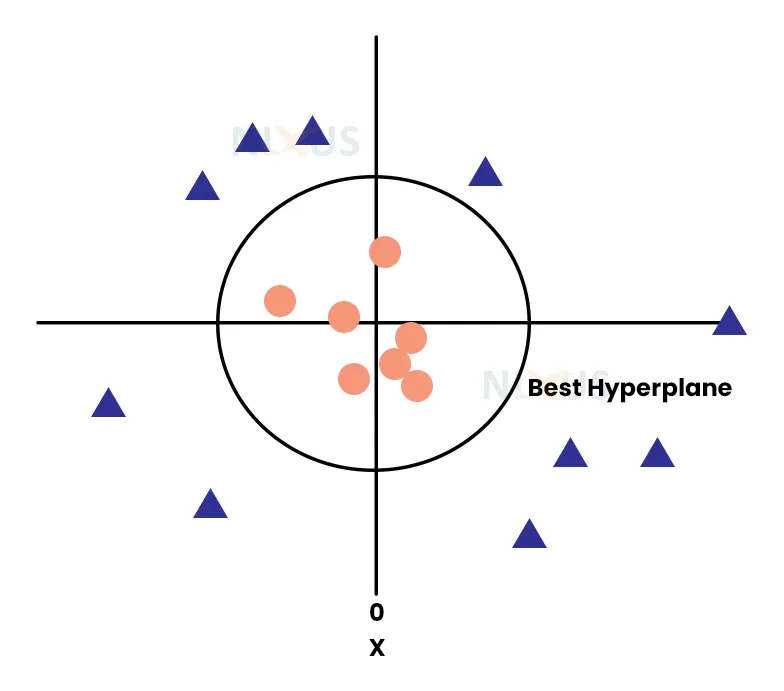
- Linear SVM– Linear SVM is for the data that we can separate linearly i.e using a line. The picture above shows an example of linear SVM classifier.
- Non-linear SVM– Nonlinear SVM is used for the data that we can’t separate linearly. We have to use non-linear functions to separate the data such as circle, ellipse, hyperbola, etc.
So, SVM works in a way that we train the model with a lot of data. SVM will draw a hyperplane according to the data that will be given to it. After that when we will give it raw data then it will try to put it on either side of the plane. And our data will be classified as green or blue depending on which side our SVM puts it on. This is how SVM works.
In our project, we are using this SVM because we have to classify whether our customer is happy or not happy with the services based on the reviews he gave. We will be using nltk because the data we are getting is in the form of text. The raw text contains a lot of extra unnecessary things that need to be removed like special characters and punctuations. These words need to be removed because they can reduce the performance of our model.
Project Prerequisites
The required modules for this project are :
- Pandas – pip install pandas
- Numpy- pip install numpy
- Sklearn- pip install sklearn
- Nltk – pip install nltk
- re- pip install re
Python Sentiment Analysis Project
For your convenience, we have already divided the dataset into training and testing data. The dataset is in the form of a CSV file. The CSV file contains the reviews column which contains reviews in sentence form. Please download the sentiment analysis python code along with the dataset from the following link: Sentiment Analysis Project
Steps to Implement Sentiment Analysis Project in Python
1. Import the Modules and read the reviews CSV file.
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder
import nltk
import string
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import CountVectorizer
from sklearn import svm
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV
import re
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import TfidfVectorizer
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
from sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import CountVectorizer
from sklearn import svm
df = pd.read_csv('train.csv')
2. Here we are labeling the hotel reviews as 0 or 1.
0 – ‘happy’ and 1 – ‘not happy’
df.shape df = df.drop_duplicates(keep='first') encoder = LabelEncoder() df['Is_Response'] = encoder.fit_transform(df['Is_Response']) df.shape
3. Here we are dropping the useless columns such as ‘user_id’, and ‘browser_used’. Because we don’t need these columns. We will just analyze the sentences.
df.drop(columns = ['User_ID', 'Browser_Used', 'Device_Used'], inplace = True)
4. Here we are removing any type of special character that is there in the sentence. We are also converting the sentences to lower_case. After doing this, we are storing the result in a new column named ‘imp_features’.
def get_importantFeatures(sent):
sent = sent.lower()
sent = re.sub('\W+',' ', sent)
return sent
df['imp_features'] = df['Description'].apply(get_importantFeatures)
df
5. Here we are using the train_test_split function of sklearn and dividing our dataset into test and train.
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split x = df.imp_features y = df.Is_Response x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(x, y, test_size = 0.25, random_state = 100) print(x_train.shape) print(x_test.shape) print(y_train.shape) print(y_test.shape)
6. Here we are creating our model SVM. After creating the model we are just fitting the training set into the model.
vector = CountVectorizer()
xv = svm.SVC()
model = Pipeline([('vectorizer',vector),('classifier',sv)])
model.fit(x_train, y_train)
pred = model.predict(x_test)
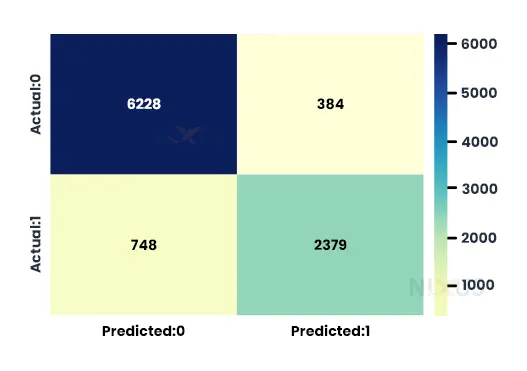
7. Our model is created and training is also completed. We have also done testing in the previous code. Here in this code, we are building a confusion matrix of the testing data using the seaborn module.
import seaborn as sns import matplotlib.pyplot as plt cm=confusion_matrix(y_test,pred) conf_matrix=pd.DataFrame(data=cm,columns=['Predicted:0','Predicted:1'],index=['Actual:0','Actual:1']) plt.figure(figsize = (8,5)) sns.heatmap(conf_matrix, annot=True,fmt='d',cmap="YlGnBu");
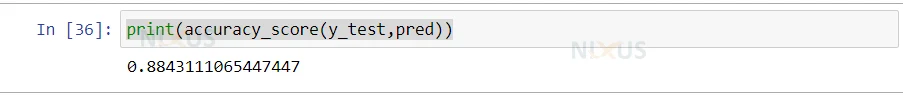
8. Here is the accuracy score between the testing and predicted data.
print(accuracy_score(y_test,pred))
Python Sentiment Analysis Output
Summary
In this Machine Learning project, we learned how to do sentiment analysis using nltk and SVM. You can also use any other method instead of SVM and see in which model you get the highest accuracy. That’s it, hope you have learned something new.